Why does the cost of a heat pump tend to be higher in colder rural areas? This is a common question that many homeowners in such regions ponder upon. A heat pump is an energy-efficient heating and cooling solution, but their performance can be affected by extreme temperatures and limited access to utility infrastructure.
In this blog post, I will explore the factors that contribute to the increased cost of heat pumps in colder rural areas. By understanding these factors, you can make informed decisions when it comes to heating your home and maximizing energy savings.
Let’s look at the details as I had experienced a $500 increase of an electric bill when we used our new pumps 2 winters ago. (On a positive note, the cost for central air condition with them is much lower.)
Understanding How It Heats
These machines are supposed to be an energy-efficient option for heating and cooling homes. They work by extracting heat from the air, ground, or water and transferring it indoors to warm your living space during the colder months.
In the summer, they can reverse the process and act as an air conditioner to cool your home. Understanding how these pumps function is essential to grasp why their costs may vary in colder rural areas.
How Does A Heat Pump Work?
Heat pumps operate on the principle of heat transfer. They consist of two main components: the indoor unit (evaporator coil) and the outdoor unit (condenser coil). Refrigerant, a substance with high heat absorption properties, circulates between these two coils.
When in heating mode, the outdoor unit absorbs heat from the outside air, ground, or water and transfers it to the refrigerant. The refrigerant then flows to the indoor unit, where it releases the absorbed heat into your home.
During cooling mode, the process is reversed. The indoor unit absorbs heat from inside your home, and the outdoor unit releases it outside, thereby cooling the indoor environment.
Efficiency Of Heating
One significant advantage of these units is their energy efficiency. Unlike traditional heating systems that generate heat, they simply transfer heat from one place to another.
This means they can provide a greater amount of heating or cooling energy than the electrical energy they consume.
The efficiency of a heat pump is measured by its Coefficient of Performance (COP). The COP represents the ratio of the heat output to the electrical energy input.
For example, one with a COP of 3 provides three times more heat energy than the electricity it consumes.
Factors Affecting Cost of Installation
Several factors can influence the cost of installation, including the size of the home, insulation levels, and the efficiency of the chosen unit. However, one of the primary factors that can impact the cost of a heat pump in colder rural areas is the difference in heating requirements.
In colder climates, they need to work harder to extract heat from the air, ground, or water sources. As the temperature drops, the available heat energy decreases, making it more challenging for them to meet the heating demands of a home.
This increased workload can result in higher energy consumption and potentially higher operating costs.
Additionally, in rural areas, where homes are often larger and spread out, the size of the heating load can vary significantly from one property to another.
Some homes may require larger, more powerful heat pumps to adequately heat or cool the space.
Factors Affecting the Cost of a Heat Pump
When it comes to installing a heat pump, the cost can vary depending on various factors. In colder rural areas, the cost of one may be higher due to specific considerations.
Let’s take a closer look at these factors and understand why they can impact the overall cost of installation.
Efficiency of Electric Heat Pumps in Cold Rural Areas
These heating machines operate by transferring heat from the outside environment to the inside of a building. In colder rural areas, where temperatures can drop significantly, the efficiency of them can be greatly affected.
The colder the climate, the harder the heat pump needs to work to extract heat from the air or ground. This increased workload may require a larger or more powerful heat pump, which can lead to higher upfront costs.
Our electric bill went up over $600 the one month we used to heat our bedroom. I still remember the look on my husband’s face when he opened that bill.
That was the last time we ever used the heat pump for heating.
Of course, the temperatures ranged from 0 to -30 degrees that week. That is the typical temperatures here in Northern Maine in January and February, and sometimes even into March.
We found it was more efficient to run an extra pellet stove vs. the heating pumps.
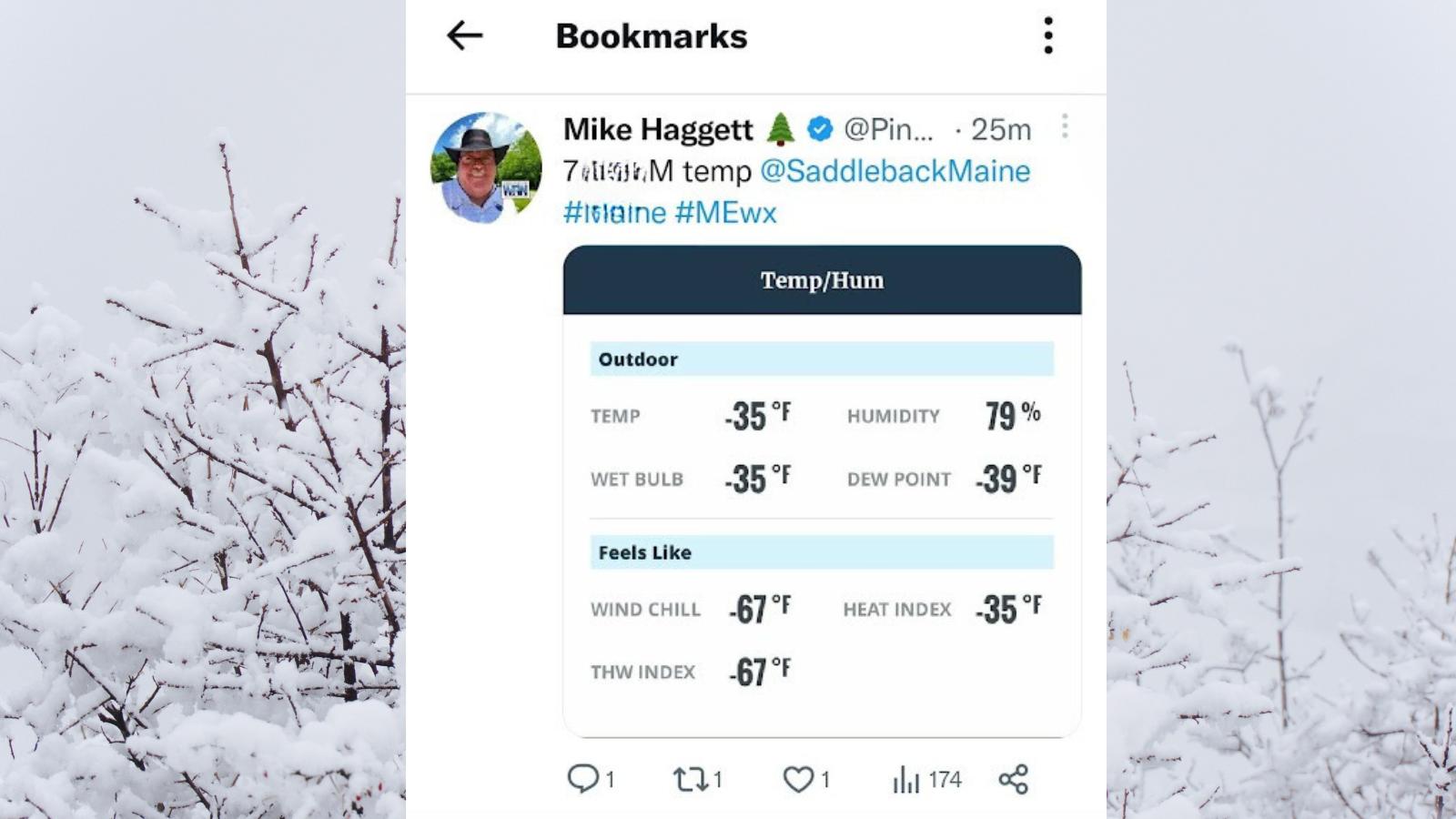
Increased Energy Demands in Colder Rural Areas
In colder rural areas, the demand for heating is typically higher compared to milder regions. This increased demand for warmth means that heat pumps in these areas need to work harder and run for longer periods to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
As a result, the energy consumption of heating systems in colder rural areas is higher, leading to increased electricity bills. These higher energy demands contribute to the overall cost of operating a heat pump in these regions.
Availability and Accessibility of Resources
Rural areas often have limited access to resources such as skilled labor, equipment, and materials. The scarcity of these resources can drive up the cost of installation.
Contractors may need to travel longer distances to reach rural areas, incurring additional transportation costs. Moreover, the availability of specific heat pump models and replacement parts can be limited in these areas, potentially leading to higher prices.
Higher Installation and Maintenance Costs
Installing a heat pump in a colder rural area can be more complex compared to urban or milder regions. The terrain, soil conditions, and the need for additional insulation may require specialized installation techniques.
These factors can increase the labor and equipment costs involved in the installation process. Additionally, the maintenance of cold-climate heat pumps in colder rural areas may require more frequent servicing due to harsher weather conditions, leading to higher maintenance costs over time.
Considering these factors, it becomes apparent why the cost of a heat pump installation can be higher in colder rural areas. The efficiency challenges, increased energy demands, limited resources, and specialized installation and maintenance requirements all contribute to the overall cost.
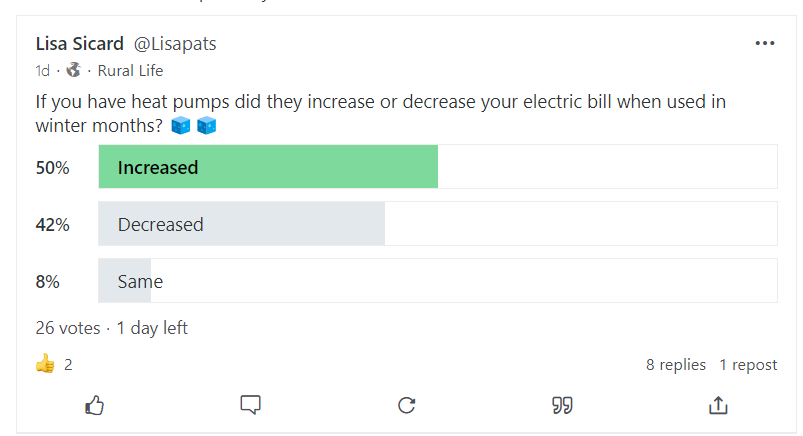
Here is a poll I took from a rural group over on Gab:
Importance of Proper Sizing and Insulation
In areas with colder climates, such as rural regions, the cost of a heat pump may be higher due to various factors. One of the key aspects that significantly impact the efficiency and cost of a heat pump is proper sizing.
Additionally, the level of insulation in these colder rural areas plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal heat retention.
Impact of Improper Sizing on Efficiency and Cost
When it comes to heating pumps, size matters. Installing a heat pump that is too small for your space will result in inefficiency and increased operating costs. On the other hand, opting for a larger heat pump than necessary can lead to unnecessary expenses during installation and higher energy consumption.
An undersized heat pump will struggle to meet the heating demands of the space, especially in colder rural areas. It will have to work harder and run for longer periods to reach the desired temperature, resulting in reduced energy efficiency and higher electricity bills.
Additionally, an undersized system may wear out more quickly due to constant overexertion, potentially leading to costly repairs or premature replacement.
Conversely, an oversized heat pump will cycle on and off more frequently, which is known as short cycling. This cycling not only reduces energy efficiency but also leads to temperature fluctuations and discomfort.
Moreover, the frequent on/off cycling can put unnecessary strain on the components of the heat pump, leading to potential malfunctions and costly repairs.
Importance of Adequate Insulation in Cold Rural Areas
In cold rural areas, where temperatures can drop significantly, having adequate insulation is paramount for efficient heating. Insulation acts as a barrier between the indoor and outdoor environments, preventing heat loss and keeping the interior warmer for longer periods.
Without proper insulation, a considerable amount of heat generated by the heating pump will escape through walls, roofs, floors, and windows. This heat loss not only reduces the overall efficiency of the pump but also forces it to work harder to compensate for the heat escaping, leading to increased energy consumption and higher bills.
By ensuring proper insulation, you can create a thermal envelope within your home, essentially trapping the heat indoors and preventing cold drafts from entering. This thermal barrier not only helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature but also reduces the load on the heat pump, allowing it to operate more efficiently and effectively.
When it comes to insulation, key areas to focus on include:
- Walls: Adding insulation to exterior walls helps prevent heat loss through them.
- Attic: Insulating the attic helps prevent warm air from escaping through the roof.
- Floors: Insulating floors above unconditioned spaces, such as garages or crawl spaces, helps prevent heat loss through them.
- Windows and Doors: Properly sealing and insulating windows and doors helps prevent drafts.
Additional Considerations for Cold Rural Areas
Living in a cold rural area presents unique challenges when it comes to installing and maintaining a heat pump. In addition to the general factors to consider, such as size, efficiency, and cost, there are specific considerations that must be taken into account in these regions.
Let’s explore two important aspects: snow removal and ventilation requirements, and backup heating systems.
Snow Removal and Ventilation Requirements
Heavy snowfall is a common occurrence in colder rural areas, and it can pose a challenge to heat pump installations. When installing a heat pump, it is crucial to ensure proper snow removal and ventilation to maintain its efficiency and functionality.
Snow accumulation around the outdoor unit can obstruct airflow and restrict its ability to operate optimally. This can lead to reduced heating performance and potential damage to the unit. Regular snow clearing is essential to prevent these issues.
One effective way to minimize snow accumulation is by elevating the outdoor unit on a platform or stand. This helps to keep the unit above the snow level, allowing for proper airflow and preventing snow from blocking the vents.
Additionally, creating a clear path for snow removal personnel to access the unit easily is important for timely maintenance and repairs.
This enables the heat pump to draw in and release air efficiently, maximizing its heating capacity and preventing issues caused by inadequate ventilation.
Backup Heating Systems
While heat pumps are an efficient primary heating solution, the extreme cold temperatures experienced in colder rural areas may require the use of a backup heating system. This backup system provides an extra source of heat when the heat pump alone may struggle to meet the heating demands.
One commonly used backup heating system is a furnace. Furnaces can provide high heat output and are capable of quickly raising the indoor temperature, making them ideal for extremely cold weather conditions.
They can seamlessly integrate with the heat pump system, automatically switching to the backup heat source when necessary.
Another option for backup heating is a dual-fuel system, which combines a heat pump with a gas or propane furnace. This system optimizes energy efficiency by utilizing the heat pump’s capabilities in milder weather and automatically activating the backup furnace during colder periods.
However, the use of pellet stoves and woodstoves is very common in our rural town. They work well and cost less than the expensive electric bills from the heating pumps in the wintertime.
We go through 6 tons of pellets during the winter months alone.
Financing Options and Incentives
When it comes to installing a heat pump in colder rural areas, the increased costs can be a concern for homeowners. However, there are financing options and incentives available that can help offset some of the expenses.
Government Rebates and Incentive Programs
Many government entities recognize the importance of transitioning to more energy-efficient heating systems, especially in colder rural areas. As a result, they offer various rebates and incentive programs to encourage homeowners to invest in heat pumps.
These programs can help reduce the upfront costs of purchasing and installing a heating pump, making it a more affordable option.
To find out what government rebates and incentives are available in your area, you can start by visiting the official websites of your local, state, and federal governments. These websites often provide detailed information on eligibility criteria and application processes.
Additionally, contacting your energy provider or local municipality can also provide valuable information on available programs.
Financing Options For Installation
In addition to government rebates and incentives, there are financing options specifically designed to assist homeowners with the installation costs of these pumps. These financing options offer flexibility and convenience for homeowners who may not have the means to pay for the system upfront.
One common financing option is through specialized financing programs. These programs often provide low-interest or even zero-interest loans that can be paid back over a specified period.
By spreading the costs over time, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of them without straining their budget.
Another option is to explore home improvement loans or lines of credit. These financial products can be used to fund installations and may offer favorable interest rates and repayment terms.
Researching and comparing different loan options can help homeowners find the most suitable financing solution for their needs.
Conclusion: The Cost Of Heat Pumps
In conclusion, it is important to understand why the cost of these heating pumps may be higher in colder rural areas. The primary reason for this is the increased demand for heating during cold weather seasons, which leads to higher operating costs.
Additionally, the remote location of rural areas often results in higher transportation and installation expenses. Moreover, the need for more powerful pumps in colder climates further adds to the overall cost.
By carefully evaluating the specific requirements and consulting with professionals, homeowners in colder rural areas can make informed decisions and choose the most suitable heating solution for their heating needs during cold long winters.
Your Turn
Have you used heating pumps to heat your home? What has your experience been with the cost of operating them? I’d love to hear more in the comments below.




